2023年4月15日
Bottleneck代码阅读
YOLOX
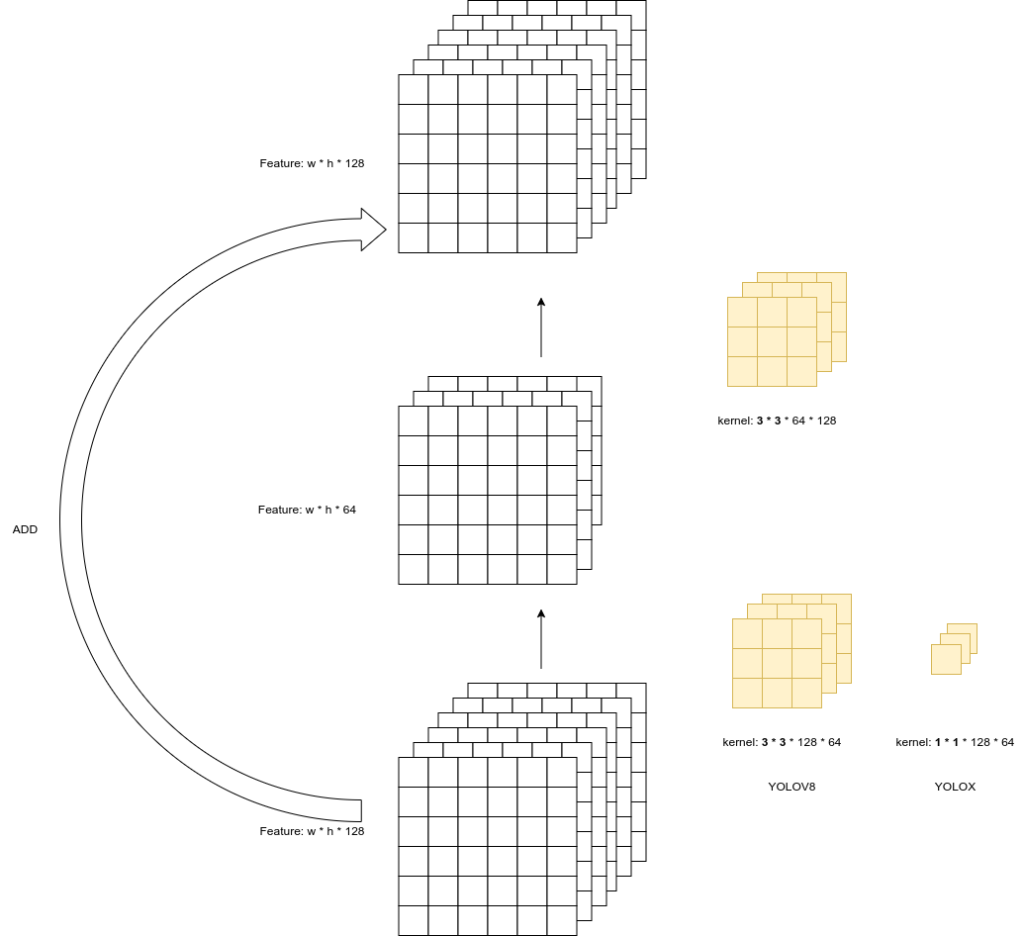
# Bottleneck的中文意思是瓶颈,瓶颈的作用是将输入的特征图的通道数从in_channels变为out_channels# 之所以使用瓶颈,是因为在yolov5中,使用瓶颈可以减少计算量,同时也可以提高模型的精度class Bottleneck(nn.Module): # Standard bottleneck def __init__( self, in_channels, # 输入通道数 out_channels, # 输出通道数 shortcut=True, # 是否使用shortcut expansion=0.5, # 通道数的扩张倍数 depthwise=False, # 是否使用深度可分离卷积 act="silu", # 激活函数,默认使用silu,也可以使用relu或者lrelu,即LeakyReLU ): super().__init__() hidden_channels = int(out_channels * expansion) # hidden_channels = out_channels // 2 Conv = DWConv if depthwise else BaseConv # 卷积层使用DWConv还是BaseConv,其中DWConv是深度可分离卷积 self.conv1 = BaseConv(in_channels, hidden_channels, 1, stride=1, act=act) # 1x1卷积,将通道数降低一半 self.conv2 = Conv(hidden_channels, out_channels, 3, stride=1, act=act) # 3x3卷积,将通道数恢复到原来的大小 self.use_add = shortcut and in_channels == out_channels # 是否使用shortcut,如果输入输出通道数相同,则使用shortcut,否则不使用,这里的shortcut是指y=y+x,即将输入的特征图和卷积后的特征图进行相加
def forward(self, x): y = self.conv2(self.conv1(x)) # 1x1卷积,3x3卷积 if self.use_add: # 如果使用shortcut,则将输入的特征图和卷积后的特征图进行相加 y = y + x # shortcut return y# Bottleneck的数据流图如下:# x -> conv1(1x1) -> conv2 -> y# |______________________|# 其中conv1是1x1卷积,conv2是3x3卷积# W*H*C -> W*H*C/2 -> W*H*C -> W*H*C# 通道数从C变为C/2,然后再变为CYOLOV8
class Bottleneck(nn.Module): """Standard bottleneck."""
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5): """Initializes a bottleneck module with given input/output channels, shortcut option, group, kernels, and expansion. """ super().__init__() c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k[0], 1) self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, k[1], 1, g=g) self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x): """'forward()' applies the YOLO FPN to input data.""" return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))